Last month, I attended Dreamforce 2024, the world’s largest software conference, in San Francisco. This massive annual event is always a great learning experience. Dreamforce’s 2024 key announcement was a New AI Era with Agentforce.
Agentforce is synonymous with AI Agent. As I explained in my previous blog about AI agents, I will explain Agentforce in the context of Salesforce/MuleSoft.
The study found that 90% of businesses say that their industry has become more competitive in the last three years, and 48% say it has become much more competitive. This led to decreased margins, force to more productivity, and transformed businesses to remain relevant in the market for any industry.
So the question is, how do we close this gap and become relevant to the market for any industry?
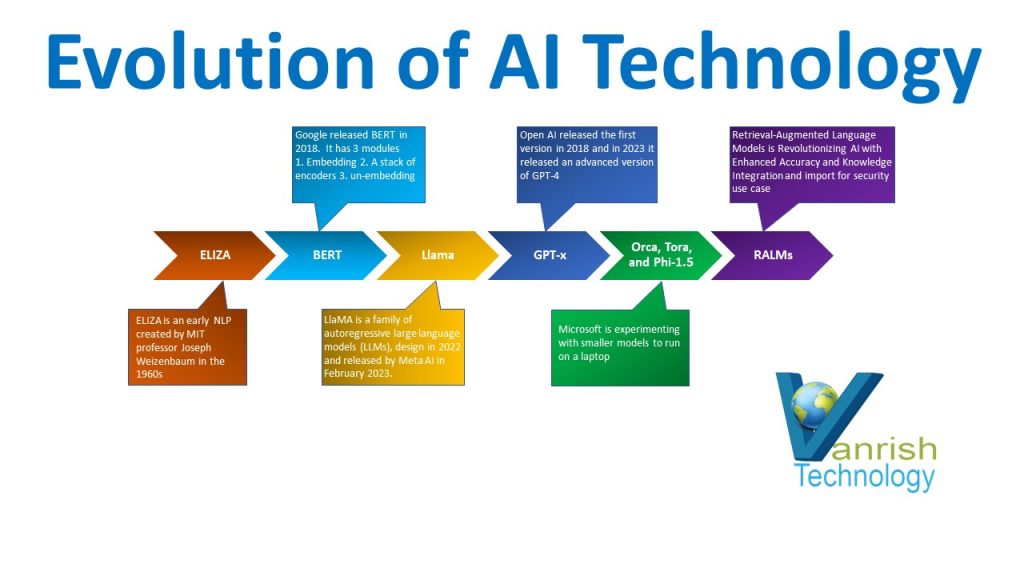
We started the AI journey with Predictive analytics as the first wave of AI. Next, we move into the Generative AI wave. Now we are next inflection point as Agentforce or AI agent. So AI Agent is waiting for us to ultimately close this gap and of course, the way that we’re going to do this is to get more time back, more productivity, and have more business growth with AI agents.

So here are a few queries, I am trying to explain
What is Agentforce?
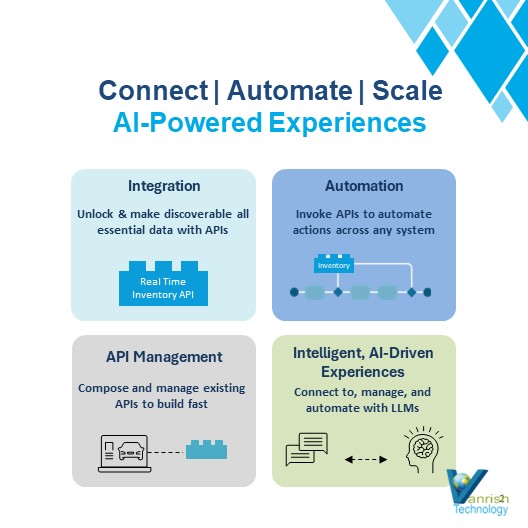
The newest Salesforce tool allows customers to build and customize autonomous agents to scale their workforce. It is a UX for customers to leverage with their data sources to deliver more human-like interactions.
How does Agentforce help customers achieve business goals?
Agentforce gives companies a 24/7 agent to engage on their behalf to resolve sales, service, and marketing-related.
topics including customer service cases and prospect engagement.
With Agentforce, companies can drive productivity to deliver higher profitability, while building stronger customer relationships.
How does MuleSoft enhance Agentforce?
Salesforce primarily focuses on the front end “human assistant” type of agents with the Agentforce UX, while MuleSoft primarily focuses on back-end domain expert agents who manage domain complexity (inventory, payroll.) and power other prompts or agents.
MuleSoft expands the actionability of the Agentforce agent by providing API actions and other domain assets for
broader context to the role, knowledge, actions, guardrails, and channel.
How are customers accessing data for Agentforce?
The Agentforce messaging encourages customers to use Data Cloud to bring in their data and ground Agentforce. To add MuleSoft into this conversation, leverage our value prop for MuleSoft + Data Cloud; where MuleSoft accelerates value against four use cases (on-premises, transactional, unstructured, activation):
● On-premise data: MuleSoft can run locally and stream data to Data Cloud, giving Agentforce additional context for improved grounding and better decision making.
● Transactional data: Transactional systems will want queuing, error handling, and delivery controls for ingestion
— functionality MuleSoft can easily deliver so that Agentforce agents aren’t slowed down.
● Unstructured data: MuleSoft offers pre-built accelerators for unstructured data ingestion to Google Drive,
Confluence, and SharePoint as well as OCR for images. Agentforce agents can have immediate access to data
from scanned images like government identification.
● Activation: Use MuleSoft to respond to data events in Data Cloud and drive action in real time to any downstream system for full circle updates.
What is the agent use cases that MuleSoft supports?
● Service Agents: Agentforce needs contextual data from external systems in order to deflect cases faster
● Sales Agents: MuleSoft can upload, and share leads from and with partners without compromising data integrity, securely with your governance rules. Near real-time synchronization with external systems ensures that Agentforce can engage with prospects starting at the moment leads come in.
● Commerce Agents: Setting up and managing storefronts requires data from external systems including product information, inventory levels, and pending vendor shipments. MuleSoft connects to external systems for near real-time updates so Agentforce can respond with accurate information.
● Employee Service Agents (Workday): Automating onboarding and provisioning for new hires requires data from external systems, and in some cases is unstructured data found in pdf, jpg, and png files like scanned government I.D.s and manually filled out forms. MuleSoft’s Intelligent Document Processing makes it easier to upload unstructured data so that you can share it faster with Agentforce.
How is Agentforce different from the MuleSoft AI Chain (MAC) Project?
MAC Project mainly targets a technical person, i.e. MuleSoft users and developers. With the MAC Project, customers can create powerful agents, fully composed in the MuleSoft Anypoint Platform and benefit from its End-to-End Lifecycle Governance and Management capabilities. With API Management, you can sprinkle it on top of LLM specific policies, to further implement the security aspects when interacting with LLMs. MAC Project is an open source project, which is currently being productized. Agentforce is more for non-technical users who wants to build powerful agents directly in Salesforce. It is fully integrated into every Salesforce Cloud and provides out-of-the-box integration to the Salesforce ecosystem.
Rajnish Kumar, the CTO of Vanrish Technology, brings over 25 years of experience across various industries and technologies. He has been recognized with the “AI Advocate and MuleSoft Community Influencer Award” from the Salesforce/MuleSoft Community, showcasing his dedication to advancing technology. Rajnish is actively involved as a MuleSoft Mentor/Meetup leader, demonstrating his commitment to sharing knowledge and fostering growth in the tech community.
His passion for innovation shines through in his work, particularly in cutting-edge areas such as APIs, the Internet Of Things (IOT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) ecosystem, and Cybersecurity. Rajnish actively engages with audiences on platforms like Salesforce Dreamforce, World Tour, Podcasts, and other avenues, where he shares his insights and expertise to assist customers on their digital transformation journey.