Introduction
A Journey from Embedded Gen AI Apps to Autonomous Agents
The evolution of AI applications, particularly in generative AI, is shaping an intriguing path for Salesforce. This progression can be divided into three key stages:
Stage 1: Embedded Generative AI Apps
Incorporating generative AI models into current applications marks the beginning of an exciting phase. These models, tailored for specific tasks, elevate the fundamental capabilities of the applications. Initially, the focus was on integrating the first wave of GPT apps, which primarily consisted of embedded Generative AI functionalities like Email Generation, Service Replies, and Work Summaries.
Key characteristics:
- Task-specific Apps
- Tight integration with existing applications
- Limited autonomy
- User interface-driven interactions
Stage 2: Conversational Apps with Einstein Copilot
As AI models advance, the focus shifts towards developing conversational applications leveraging Copilot technology. These intelligent assistants are adept at interpreting and addressing Stage 2: user inquiries using natural language. Capable of executing various functions, from offering information to handling intricate tasks.
Key characteristics:
- Conversational interface
- AI Agent as the central intelligence
- Expanded capabilities beyond task-specific functions
- Increased user autonomy
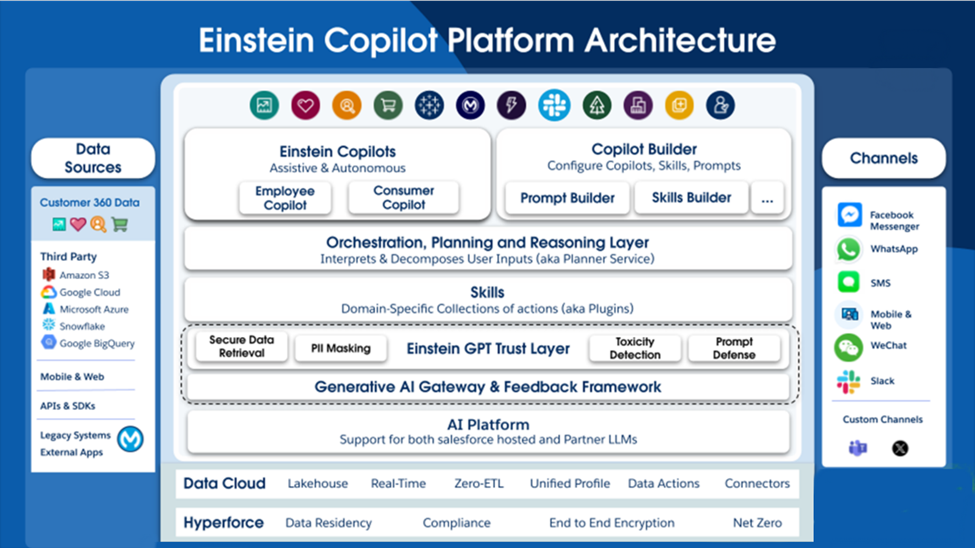
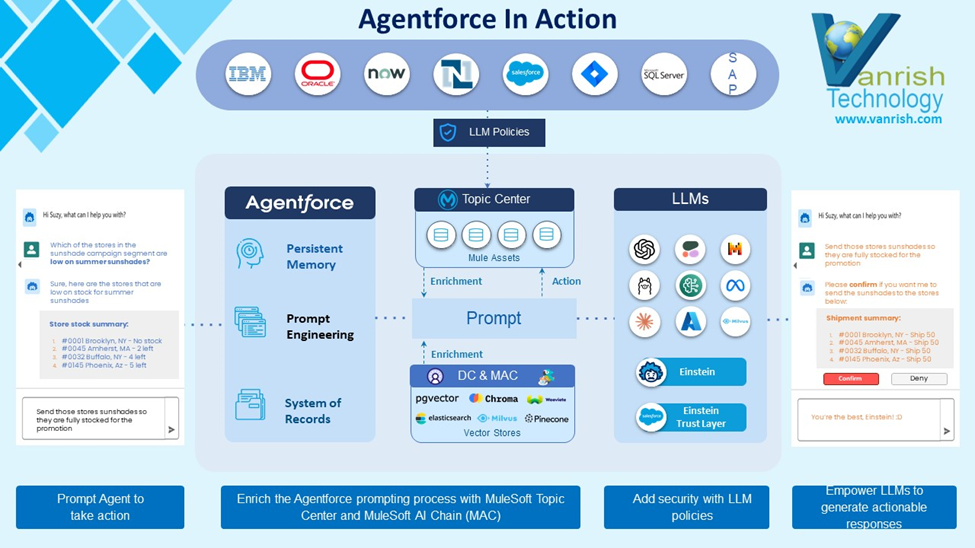
Stage 3: Agent Force Platform & Autonomous Agent/Agents
In the third stage, the Salesforce platform transitioned from a single Agent to multiple Agents, implementing changes to achieve this through the Agentforce Platform. The Agent Force Platform now includes the Agent RAG feature as a standard offering for all Agents. This update brings enhancements like topic filtering, Agent headless APIs, and other improvements to streamline operations and boost efficiency.
A framework outlines how clouds can build their own autonomous agents using the Agent Force Platform featuring a flexible UI and comprehensive testing capabilities. As part of autonomous agents
It also added how these AI agents operate independently without a user interface, proactively identifying and executing tasks based on predefined goals or real-time data. They seamlessly integrate with diverse systems and applications to streamline operations and attain specific outcomes.
Key characteristics:
- Proactive task initiation and execution
- Integration with multiple systems
- Continuous learning and improvement
- Potential for automation of complex workflows
Rajnish Kumar, the CTO of Vanrish Technology, brings over 25 years of experience across various industries and technologies. He has been recognized with the “AI Advocate and MuleSoft Community Influencer Award” from the Salesforce/MuleSoft Community, showcasing his dedication to advancing technology. Rajnish is actively involved as a MuleSoft Mentor/Meetup leader, demonstrating his commitment to sharing knowledge and fostering growth in the tech community.
His passion for innovation shines through in his work, particularly in cutting-edge areas such as APIs, the Internet Of Things (IOT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) ecosystem, and Cybersecurity. Rajnish actively engages with audiences on platforms like Salesforce Dreamforce, World Tour, Podcasts, and other avenues, where he shares his insights and expertise to assist customers on their digital transformation journey.

